MDF doesn’t handle moisture very well, it is more suited for indoor use such as in furniture. Also due to its non-directional grain structure, MDF is ideal for cutting, machining and drilling without splinters or chipping.
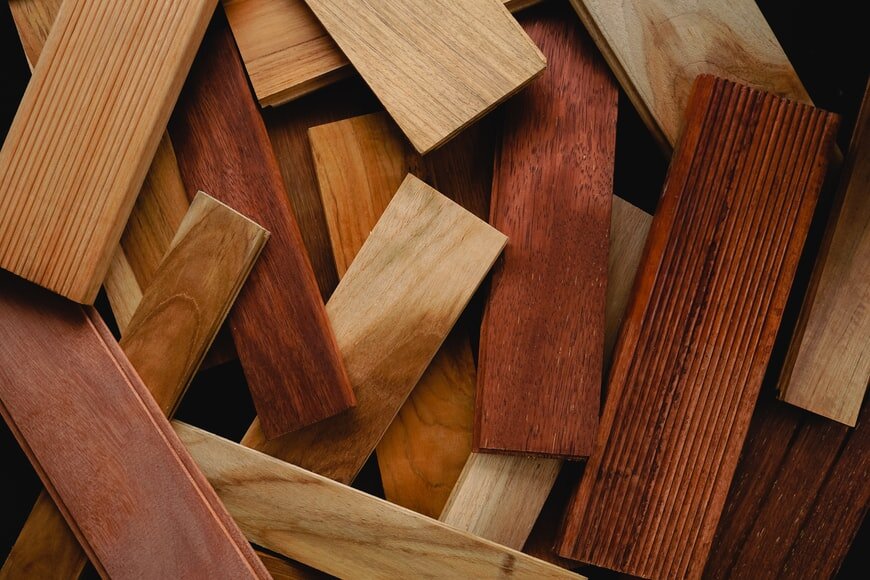
Plywood is generally used for doors, stairs, flooring and exterior projects but also bends easily with the grain, so it is often used to create curved surfaces.
MDF
MDF (Medium Density Fibreboard) is an engineered material made by breaking down hardwood or softwood residuals into fine particles, combining it with wax and a resin binder and applying high temperature and pressure.
Advantages of MDF
- MDF is typically less expensive than plywood.
- The MDF surface is quite smooth, and there are no knots on the surface.
- It’s a terrific surface for painting because it’s so smooth. It is recommended to start using it with a high-quality oil-based primer. (Avoid spraying aerosol primers on MDF! It just absorbs, resulting in a significant loss of time and money.)
- MDF wood is also an excellent veneer substrate because of its smoothness.
- Because MDF material is fairly consistent, the cut edges seem smooth and devoid of gaps or splinters.
- Because of the clean edges, a router may be used to produce ornamental edges.
- The MDF’s uniformity and smoothness make it easier to cut elaborate designs (such as a roll or cut design) with a scroll saw, band saw, or jigsaw.
Disadvantages of MDF
MDF like every other material has a set of drawbacks:
- MDF absorbs water and other liquids like a sponge and expands if not properly sealed.
- Because MDF is a solid material, it is heavy and difficult to work with.
- Because it is made of fine fibre, it does not retain screws very well.
- MDF is readily damaged and sags if not handled with care.
Plywood
Plywood is also an engineered wood product, made by pressing and binding sheets of wood veneer together into one solid piece.
Lower grades are used in the construction of houses. The higher grades of plywood (stain grade, cabinet grade, etc.) are much prettier and smoother.
Unlike MDF, they have consistent wood grain showing and generally lack knot holes and other major imperfections.
Advantages of plywood
- Made from multiple layers of wood veneer, plywood is a very strong material to work with.
- It won’t soak up water and liquids as quickly or easily as MDF does so it’s less susceptible to water damage.
- Because it carries a grain, plywood is stainable. Which makes it perfect for kitchen cabinets, tabletops and other projects where you want a large stained wood surface.
- It is less prone to water damage than MDF, as it does not absorb water and does not swell as rapidly or readily.
- It’s environmentally friendly, making it ideal for kitchen cabinets, tables, and other tasks requiring a big stained wood surface.
- Although most plywood includes urea-formaldehyde and other VOCs, formaldehyde-free plywood is now available. At Home Depot, look for the Purebond brand.
Disadvantages of plywood
Before you leap to conclusions, here are some of the downsides of plywood that you should be aware of before purchasing it:
- Plywood costs more than MDF, and the better the grade, the higher the price.
- It is tough to make patterns using plywood since it is difficult to achieve completely clean cuts on it.
- When not cut properly, plywood splinters readily, and the edges with layers may have cavities.
What’s better MDF or plywood?